ROUTINE is a retro-futuristic horror game set in an abandoned lunar base, known for its eerie CRT aesthetics and slow-burn tension. But beneath its atmospheric brilliance lies one controversial design challenge: the game’s unique interaction delay system. Every action—opening a hatch, pulling out the Cosmonaut Assistance Tool (CAT), rewiring a panel—requires a deliberate, animated sequence. This system heightens realism but also creates friction, especially when encounters with the robotic Cleaners demand split-second decisions.
This article explores how this design choice shapes gameplay over time, how players adapt or fail to adapt to it, and why this issue both defines ROUTINE’s identity and limits its broader accessibility.
1. The First Steps: When Players First Notice Deliberate Interactions
At the beginning of ROUTINE, the interaction delay feels like part of the world-building. Opening drawers, manipulating switches, and handling old-school lunar equipment help ground the player in the tactile, analog universe the game has crafted. That early experience signals a commitment to immersion rather than speed.
But the first time players face a tense moment—hearing metallic footsteps in the distance while fumbling through a maintenance locker—the weight of delayed inputs becomes noticeable. What feels immersive at first becomes a source of anxiety and mechanical friction. The player begins to realize that ROUTINE demands not just navigation, but patience and foresight.
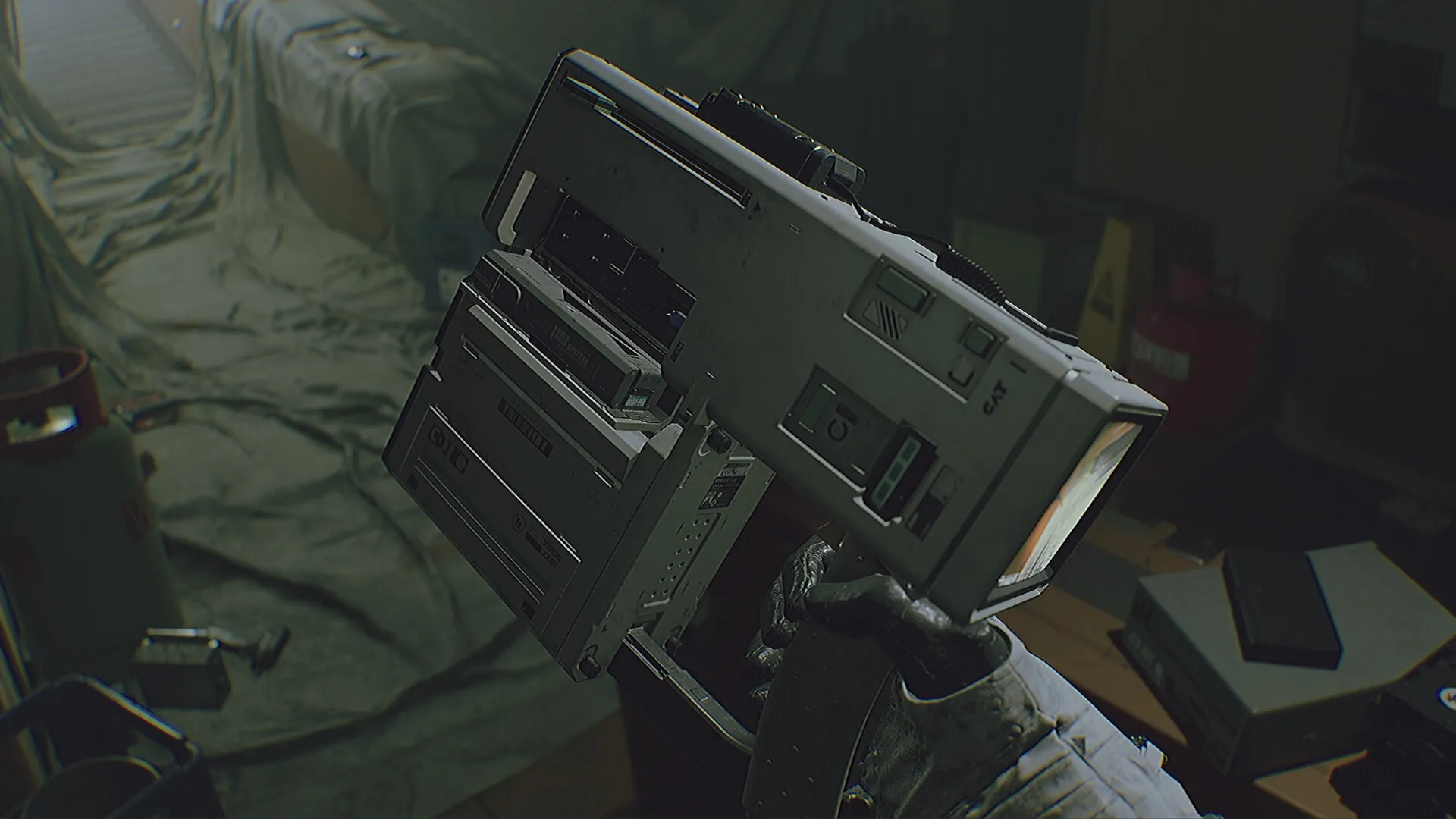

2. The Moment Responsiveness Becomes a Question
By the time players reach the early residential sector, the novelty gives way to doubt. A lingering question arises: is this system enhancing tension or actively hindering player control?
ROUTINE’s animation-first interaction model slows every gesture. Pulling open a vent requires committing to a full animation, leaving no room to cancel or react partway through. It is here that the tension between realism and responsiveness becomes a concern.
The game begins to shape new instincts—players start checking corners twice, planning routes more carefully, and avoiding unnecessary interactions. ROUTINE forces them to think not in frames, but in seconds, and this mental shift becomes a defining hurdle.
3. The Cleaners Enter: When Delays Become Deadly
The Escalation of Threat
Cleaners, ROUTINE’s autonomous android enforcers, bring the interaction delay issue into sharp focus. These machines respond quickly, stalk quietly, and execute ruthlessly. The player, meanwhile, must wait for animations to complete before reacting.
H4: The Disadvantage Triangle
Against Cleaners, interaction delay creates a three-point disadvantage:
- slow item handling
- slow environmental manipulation
- slow stance transitions
What was once immersive now feels like a systemic vulnerability. Encounters become less about skill and more about prediction—occasionally bordering on trial-and-error.
4. Mid-Game Zones and the Cumulative Weight of Delay
As players explore deeper sectors, such as Power Control and Communications, ROUTINE introduces more complex environmental puzzles. These puzzles often require multitasking—rewiring circuits while monitoring sound cues.
The interaction delay now becomes cumulative. Actions stack in the player's mind: reaching for a panel, flipping open its cover, selecting the right tool. Each step introduces a delay that transforms a simple task into a calculated gamble. The fear no longer comes solely from enemies, but from time itself.
At this stage, the issue becomes thematic: is the game intentionally forcing players to live with the consequences of being a fragile human among mechanical predators, or is the system artificially restricting agency?
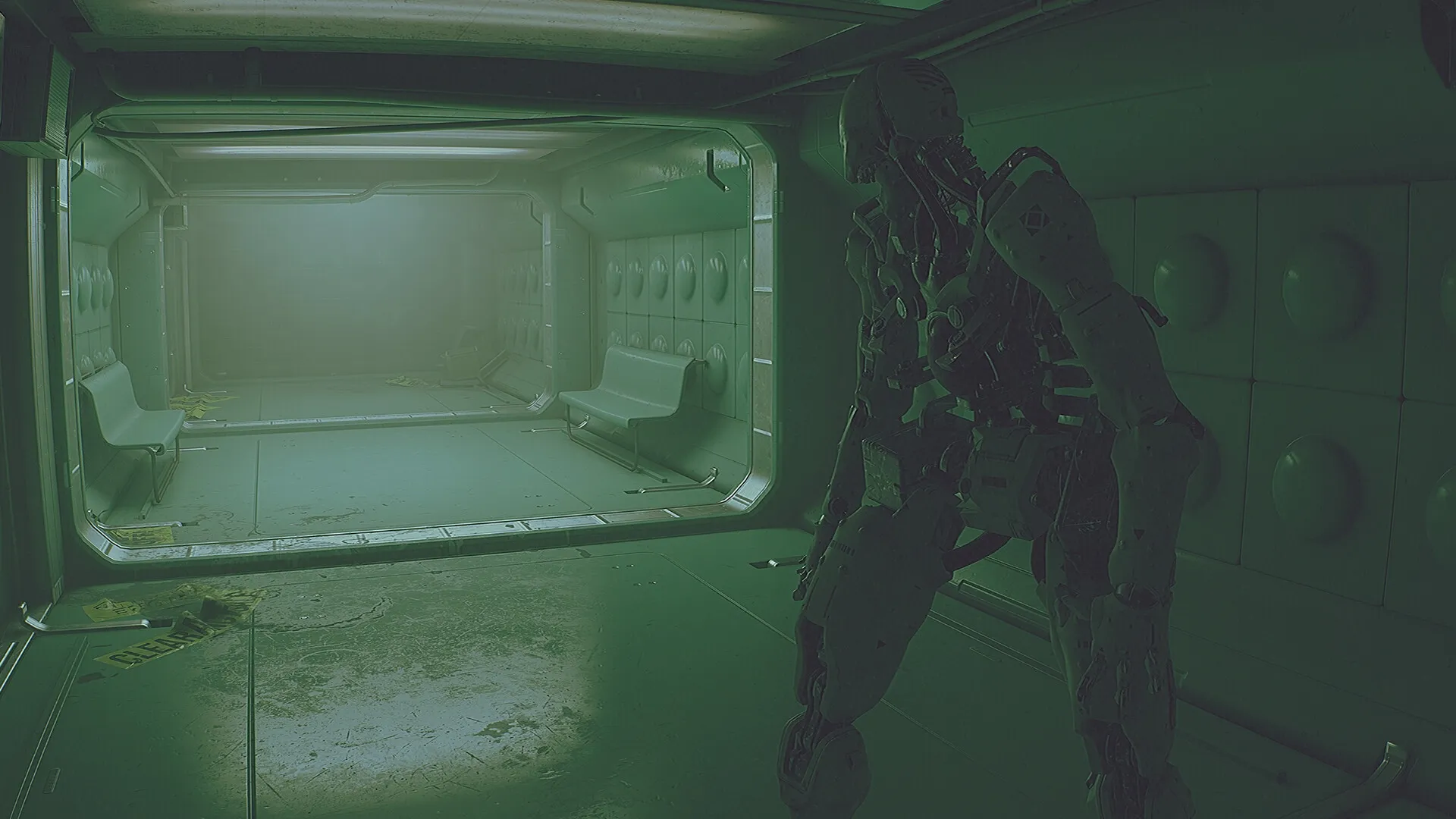

5. Decision Paralysis: How Players Change Their Behavior
Adaptation Patterns
Players develop new behavioral patterns to cope with delay. They may:
- pre-open doors to avoid mid-chase interactions
- maintain a fixed rotation route to reduce unexpected decisions
- avoid optional areas, fearing animation vulnerability
These adaptations reveal a shift from exploration to preservation. Instead of engaging with ROUTINE’s rich details, players begin trimming their own freedom to reduce risks created by the interaction system.
H4: The Emotional Consequence
Tension becomes exhaustion. What begins as cinematic immersion evolves into mental over-planning, diminishing spontaneity.
6. Emotional Tension vs. Mechanical Friction: A Core Conflict
The central issue of ROUTINE’s interaction delay is this: the system produces amazing tension but creates mechanical friction.
The horror genre thrives on vulnerability, but ROUTINE pushes vulnerability into territory that sometimes disrupts play rather than supports it. Players struggle to distinguish between fear derived from good design and fear derived from lost control.
This conflict becomes more pronounced in later sections where pacing tightens. The game’s strongest narrative moments sometimes clash with its most restrictive mechanical features.
7. The Learning Curve: Mastery or Resignation?
As hours pass, players fall into two camps: mastery and resignation.
H3: Mastery
Some players learn to “think in delay.” They anticipate, pre-plan, and move rhythmically with the game’s pacing. For these players, the system becomes an advantage; it reinforces the slow, dreadful ambiance.
H3: Resignation
Others feel constrained. They view delay as a forced handicap, an obstacle to enjoying the world. For them, Cleaners become less frightening enemies and more reminders of the system’s imbalance.
This duality creates a fractured community experience. ROUTINE becomes a game not everyone can experience fluently, not because of difficulty, but because of pacing.
8. Endgame Pressure and the Intensification of Delay Consequences
In late-game sectors like Lower Engineering, enemies patrol aggressively and environmental hazards increase. Here, ROUTINE tests every habit players have formed.
Slow panel interactions become life-or-death decisions. Turning around takes time. Equipping the CAT requires a full animation that can betray a player’s position.
The pressure amplifies the system's flaws. The design intent—to increase realism—starts to feel like a hindrance to the climactic pacing. At the moment when tension should peak naturally, mechanical friction steals some of the emotional impact.
9. The Player-System Relationship: A Study in Pacing Philosophy
H3: How Gameplay Shapes Story
The interaction delay affects narrative interpretation. Characters seem more vulnerable, more human, more overwhelmed. The lunar base feels heavy and oppressive.
H3: How Story Shapes Gameplay
Yet the story also suffers because of the system. Players sometimes miss narrative cues or environmental storytelling because they are too focused on avoiding interactions that might trap them in animations.
H4: The Trade-Off
ROUTINE forces a philosophical question:
Is horror more effective when players feel restricted, or when they feel empowered but terrified?
The interaction delay system argues firmly for the former, but not all players accept that argument.
10. Could the System Have Been Smarter? A Look at Alternatives
Many modern horror games implement contextual speed variations—fast interactions when threatened, slower ones during exploration. ROUTINE commits fully to slow realism, leaving no room for adaptive responsiveness.
H3: Possible Alternatives
A smarter system might have included:
- interruptible animations
- safety-padding for critical actions
- contextual acceleration based on danger level
- a predictive input queue
H4: What This Would Change
Such systems could preserve immersion while reducing frustration. They would allow ROUTINE to maintain its oppressive atmosphere without sacrificing responsiveness during high-pressure moments.
Instead, the game opts for purity—admirable in concept, divisive in execution.
ROUTINE’s interaction delay system is both its beating heart and its structural flaw. It deepens immersion, grounds the world in tactile realism, and amplifies fear. But it also burdens the player with constant vulnerability that surpasses thematic intention and enters mechanical frustration.
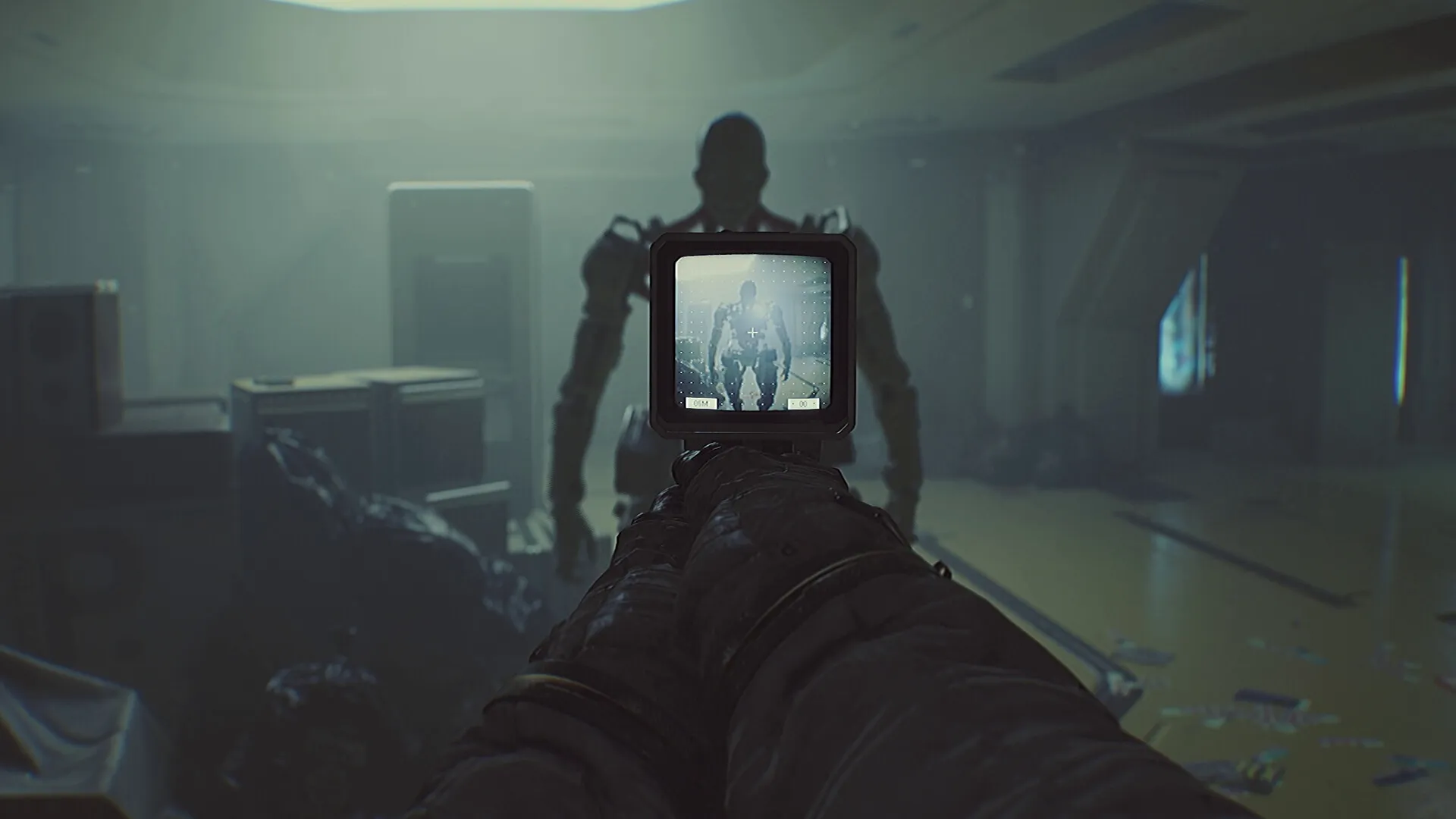

The system defines ROUTINE’s identity, shaping every encounter, puzzle, and moment of tension. Yet it also polarizes the player base, creating two radically different experiences: one shaped by mastery of delay, and one shaped by resistance to it.
By understanding this specific issue, we can appreciate ROUTINE not just as a horror game but as a bold experiment in pacing, vulnerability, and atmospheric control—one that succeeds brilliantly in some areas while creating avoidable friction in others.